Parameters for shapes and particles
![]() Particle analysis > Parameters
Particle analysis > Parameters
The parameters are the same for particles detected in the Particle analysis study, and for shapes drawn in the Manual measurements study.
Note: Most of the time, we will use the words "particle" or "feature", but keep in mind that in your field of application, other terms might be more appropriate. More information...
Note: For Ellipse and Rectangle shapes, parameters are calculated from geometrical formulae when possible.
Abbreviations used in the table
▪S: Parameters for Shapes (Manual measurements study).
▪TD: Parameters for Threshold detection method (Particles analysis study).
▪WD: Parameters for the Watershed detection method (Particles analysis study).
▪ED: Parameters for Edge detection method in (Particles analysis study).
▪CD: Parameters for Circle detection method in (Particles analysis study).
Vocabulary and definitions
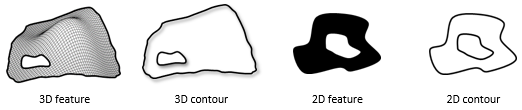
Outline |
The outline of a feature is the projection of the feature's boundaries on a 2-dimensional horizontal plane. |
Contour |
The contour of a feature is its 3-dimensional boundary, with varying Z-heights along the contour. |
Available parameters
Settings defined by the user, listed for information
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Method |
Detection methods: ▪Threshold detection ▪Watershed detection ▪Edge detection ▪Circle detection |
|
|
|
|
Particles to detect |
When using "Threshold detection", detect particles: ▪Above a threshold value ▪Below a threshold value ▪Between two threshold values ▪Outside two threshold values |
|
|
|
|
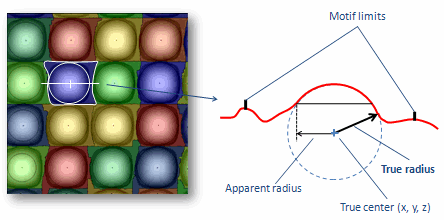
Motifs to detect |
When using "Watershed detection", detect: ▪Hill motifs ▪Dale motifs |
|
|
|
|
Features to detect |
When using "Circle detection", detect: ▪Particles (protruding objects) ▪Holes (receding objects) |
|
|
|
|
General parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Reference (for threshold) |
Reference used as a threshold |
|
|
|
|
Threshold 1 |
Custom threshold |
|
|
|
|
Threshold 2 |
Custom threshold |
|
|
|
|
Threshold |
Custom threshold |
|
|
|
|
Min diameter (for detection) |
Minimum custom diameter for circle detection |
|
|
|
|
Max diameter (for detection) |
Maximum custom diameter for circle detection |
|
|
|
|
Pruning |
Pruning type (height pruning or area pruning) and pruning values |
|
|
|
|
Number of particles |
Detected number of particles |
|
|
|
|
Density |
Density of particles |
|
|
|
|
Coverage |
Coverage in percent of the whole surface area |
|
|
|
|
Area parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Projected area |
Projected horizontal area enclosed by the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Length and distance parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Perimeter |
Projected perimeter. Length of the outline of the particle, including the perimeters of perhaps existing holes in the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
External perimeter |
Projected external perimeter. Length of the (projected) perimeter of the particle, without taking into account the perimeters of perhaps existings holes in the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Radius (circle) |
Radius of the circle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter (circle) |
Diameter of the circle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Equivalent radius |
Radius of the disk whose area is equal to the area of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Equivalent diameter |
Diameter of the disk whose area is equal to the area of the particle. Also called "Heywood diameter". |
|
|
|
|
|
Mean diameter |
Mean diameter of the particle, measured from its center of gravity. |
|
|
|
|
|
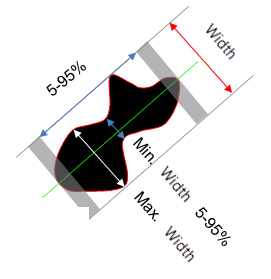
Min diameter |
Smallest diameter of the particle, measured from its center of gravity. |
|
|
|
|
|
Max diameter |
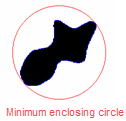
Maximum diameter of the particle, measured from its center of gravity. Note: The maximum diameter is the diameter of the minimum enclosing circle.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum caliber |
Longest distance between any two points on the particle's outline. Also called "Maximum Feret's diameter". |
|
|
|
|
|
X-extent |
Size of the particle along the X-axis. Note: X-size of the axis-oriented minimum bounding rectangle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Y-extent |
Size of the particle along the Y-axis. Note: X-size of the axis-oriented minimum bounding rectangle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Volume parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Volume |
Maximum volume (volume of material or volume of void). |
|
|
|
|
|
Volume of material |
Volume of all points having a Z-value higher than the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Volume of void |
Volume of all points having a Z-value lower than the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Local volume |
Hill: Material volume of the motif, above the highest saddle point. Dale: Void volume of the motif, below the lowest saddle point. |
|
|
|
|
|
Sphere parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Sphere |
Radius (sphere) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X of sphere center |
X-coordinate of the center of the sphere. |
|
|
|
|
|
Y of sphere center |
Y-coordinate of the center of the sphere. |
|
|
|
|
|
Z of sphere center |
Z-coordinate of the center of the sphere. |
|
|
|
|
|
Skeleton parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Skeleton |
Shape |
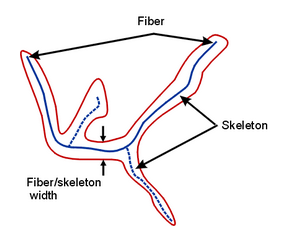
Skeleton length |
Result of thinning the particle into a one-pixel-wide line with branches. Sum of the lengths of all branches of the skeleton. Note: Ellipses are not skeletonized. Note: This parameter may increase the computation time.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiber length |
Length of the longest path in the skeleton. Relevant parameter for measuring the length of long thin shapes (e.g. DNA). Note: This parameter may increase the computation time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiber width |
Ratio between the area of the particle and the skeleton length. For a normal worm-like particle, it will be the mean width perpendicular to the fiber. Note: Should be more accurately called "Skeleton width". Note: This parameter may increase the computation time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Height parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Local height |
Hill: Height difference between highest saddle point and peak. Dale: Height difference between pit and lowest saddle point. |
|
|
|
|
|
Z-min |
Minimum Z-value of all points inside the smoothed outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Z-max |
Maximum Z-value of all points inside the smoothed outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Z-mean |
Average of the Z-values of all points inside the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Z-extremum |
Minimum or maximum Z-value inside the outline of the particle. Detection of hills: Z-extremum = Z-max Detection of dales: Z-extremum = Z-min |
|
|
|
|
|
Mean contour height |
Average Z-value of the points on the particle's contour. |
|
|
|
|
|
Min contour height |
Minimum Z-value of the points on the particle's contour. |
|
|
|
|
|
Max contour height |
Maximum Z-value of the points on the particle's contour. |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum depth |
Maximum depth inside the outline of the particle. Value relative to the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Mean depth |
Average of Z-values of all points inside the contour of the particle that are smaller than the mean contour height. Values are relative to the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum height |
Maximum height inside the outline of the particle. Value relative to the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Mean height |
Average of Z-values of all points inside the outline of the particle that are bigger than the mean contour height. Values are relative to the mean contour height. |
|
|
|
|
|
Position parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
X of Z-min |
X-position of Z-min: X-coordinate of the lowest point inside the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Y of Z-min |
Y-position of Z-min: Y-coordinate of the highest point inside the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
X of Z-max |
X-position of Z-max: X-coordinate of the highest point inside the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Y of Z-max |
Y-position of Z-max: Y-coordinate of the highest point inside the outline of the particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
X of Z-extremum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y of Z-extremum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X of geometric center |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y of geometric center |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X of gravity center / Y of gravity center |
The gravity center is based on the particle's outline.
|
|
|
|
|
|
X of gravity center (material) / Y of gravity center (material) |
Center of gravity of the material volume, i.e. for those points inside the outline of the particle with Z-values above the mean contour height. Center of gravity relevant for particles (protruding features, i.e. features above the background). |
|
|
|
|
|
X of gravity center (void) / Y of gravity center (void) |
Center of gravity of the void volume, i.e. for those points inside the contour of the particle with Z-values below the mean contour height. Center of gravity relevant for pores (receding features, i.e. features below the background) |
|
|
|
|
|
X of circle center / Y of circle center |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shape and orientation parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Edge/Interior |
▪Edge: Partial or open particle in contact with or cutting the edge of the studiable. ▪Interior: Complete particle without contact with the edge of the studiable. |
|
|
|
|
|
Form factor |
Ratio between the area of the particle and its squared perimeter. Describes the shape of a feature.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aspect ratio |
Ratio between the max diameter and the min diameter. If the value is close to 1, the form of the particle is close to the form of a disk. If the value is high, the particle is oblong.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Roundness |
Ratio between the area of the particle and the area of the disk having as diameter the max diameter of the particle. This value is close to 1 for a circular particle, and smaller than 0.5 for an oblong particle.
Note: This parameter may increase the computation time. |
|
|
|
|
|
Compactness |
Ratio between the equivalent diameter and the max diameter. This ratio is close to 1 for a particle with the form of a disk, or smaller than 0.5 for an oblong particle. Compactness = Equivalent diameter / Max diameter Note: The compactness of a circle is 1. The compactness of a square is √(2/π) ≈0.79784. |
|
|
|
|
|
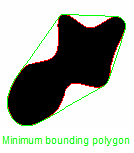
Convexity |
Ratio between the perimeter of the minimum bounding polygon (convex perimeter) (in green) and the perimeter of the particle itself (in red).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Elongation |
Indicates how elongated a particle is. A square or circle have an elongation of 0. The longer the rectangle or the ellipse, the closer the value will be to 1. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solidity |
Describes the similarity of the particle's area with its convex area. Ratio between the area and the area inside the minimum bounding polygon (convex area).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Orientation |
Angle between the biggest axis of the smoothed particle and the X-axis. Note: Angle expressed in degrees, in trigonometric direction, with 0° at the right side.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Angle of min diameter |
Angle between the X-axis and the smallest diameter of the particle (diameter measured trough the particle's center of gravity). Note: Angle expressed in degrees, in trigonometric direction, with 0° at the right side. |
|
|
|
|
|
Angle of max diameter |
Angle between the X-axis and the maximum diameter of the particle (diameter measured trough the particle's center of gravity). Note: Angle expressed in degrees, in trigonometric direction, with 0° at the right side. |
|
|
|
|
|
Length |
Length of the particle's oriented bounding rectangle. Note: The bounding rectangle is parallel to the biggest axis of the particle. For a circle: Length = Diameter For an ellipse: Length = Length of major axis |
|
|
|
|
|
Width |
Width of the particle's oriented bounding rectangle. Note: The bounding rectangle is parallel to the biggest axis of the particle. For an ellipse: Width = Length of minor axis |
|
|
|
|
|
Neighbor parameters
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Number of neighbors |
Number of adjacent particles in direct contact with the respective particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Pitch |
Hill: Mean horizontal distance between the peak of this particle and the peaks of adjacent particles. Dale: Mean horizontal distance between the pit of this particle and the pits of adjacent particles. |
|
|
|
|
|
Max pitch |
Hill: Maximum horizontal distance between the peak of this particle and the peak of an adjacent particle. Dale: Maximum horizontal distance between the pit of this particle and the pit of an adjacent particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Min pitch |
Hill: Minimum horizontal distance between the peak of this particle and the peak of an adjacent particle. Dale: Minimum horizontal distance between the pit of this particle and the pit of an adjacent particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Coflatness |
Hill: Maximum vertical distance between the peak of this particle and the peak of an adjacent particle. Dale: Maximum vertical distance between the pit of this particle and the pit of an adjacent particle. |
|
|
|
|
|
Obsolete parameters
Old parameters kept for compatibility.
Parameter |
Explanation |
TD |
WD |
ED |
CD |
Shape |
Height |
Height difference between the mean height of the smoothed particle and the lowest point of the surface. |
|
|
|
|
|