Morphological correction
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Studies tab
Studies tab ![]() Structural analysis
Structural analysis ![]()
![]() Particle analysis
Particle analysis
![]() Particle analysis > Morphological correction
Particle analysis > Morphological correction
|
Morphological correction |
Open a dialog to change the detected features by making mathematical morphology operations. |
Types of correction
The images shown hereafter are obtained from the following source image: |
|
|
Erosion Erosion discards one line of pixels around each object. |
|
Dilation Dilation adds one line of pixels around each object. |
|
|
|
|
Opening Opening consists in applying a dilation and an erosion one after another which results in opening the objects and separating grains hardly touching one another. |
|
Closing Closing consists in applying an erosion and a dilation one after another which results in closing the objects and in melting the grains hardly touching one another. |
Conditions
Strength |
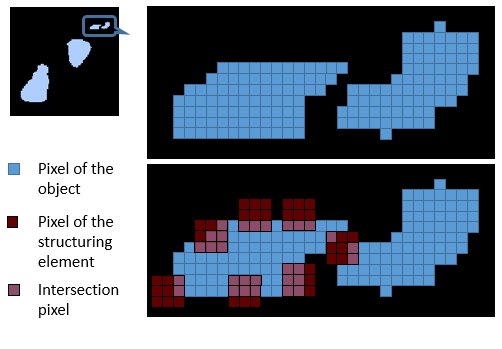
Strength or sensitivity of the morphological operation. A 3x3 square is used as a structuring element. When the square moves over the image, at a given position, there is an intersection of 0 to 9 of its pixels with the pixels of the image's object.
▪When choosing the maximum strength of 4, an intersection with only 1 pixel of the structuring element is enough to add a pixel to the object (dilation). or to discard a pixel from the object (erosion). ▪When choosing the strength of 1, an intersection with at least 4 pixels is needed to discard or add a pixel. |
Iteration |
Number of times the correction is applied. Max. value: 5 |
Remove grains touching the edges
If you check this option, the resulting image will be freed from all the grains touching one of the image edges. This enables you to work only on whole objects that are not cut by the edges of the image.
Merge contiguous grains
If two or several grains touch each other after the correction, these contiguous grains can be merged into a single bigger grain.