Surface Metrology Quiz #1
How much do you know about surface metrology? This quiz covers topics such as: areal surface texture, areal field parameters and profile parameters. Help is at hand if you get stuck as all the answers are to be found in the pages of our Surface Metrology Guide
Question 1: Which of the following parameters are related to the height distribution?
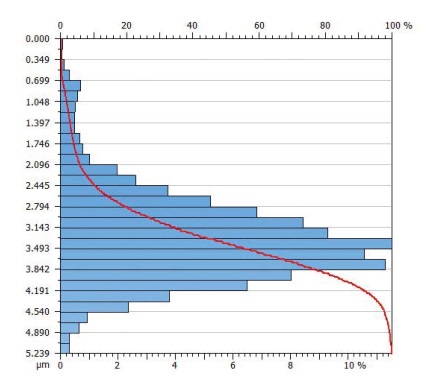
A Rz
B Rq
C Rsk
D Rmr
Question 2: Which of the below height distribution graphs corresponds to a negative skewness?
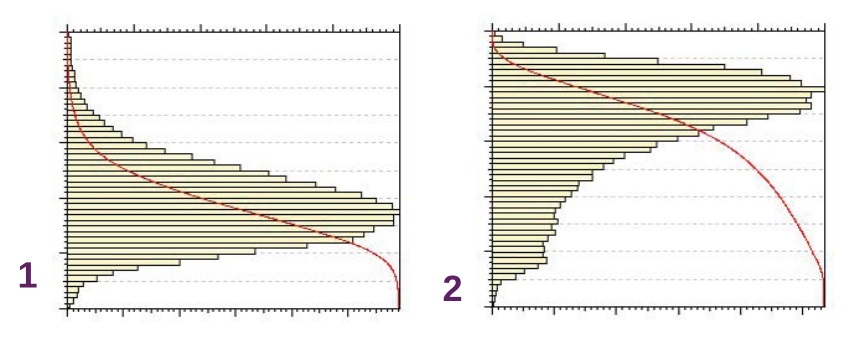
A Graph 1
B Graph 2
C Neither
Question 3: Which of the following statements are true?
A It is mandatory to use a Gaussian filter for roughness parameters
B Some surface texture parameters can be calculated without any filter
C Without any specific indication, the Gaussian filter should be used
D The Gaussian filter is best used on structured and stratified surfaces
Question 4: Which of the following instrument technologies have a dedicated document in the new areal standard?
A White-light interferometry
B Fringe projection
C Areal stylus profilometry
D Chromatic confocal probe
E Scanning electron microscopy
F Confocal microscopy
Question 5: In which of the following cases it is necessary to evaluate surface texture on a surface instead of on a profile?
A When the surface is isotropic
B When the surface is structured
C When the surface contains scratches in various directions
D When the surface has very small grains equally distributed
E When the surface has big grains/holes unequally distributed
F When roughness is above 10 µm
Question 6: Feature parameters are areal parameters...
A that are not related to surface heights
B that quantify topological features
C that do not take into account all surface points
D that are calculated after a height discrimination
Question 7: Wolf pruning is...
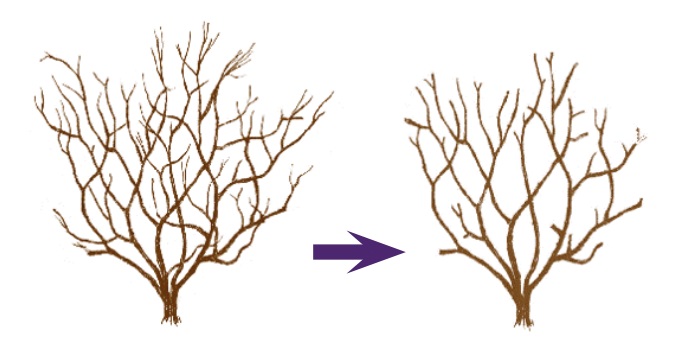
A used in the calculation of spacing parameters
B used in segmentation, to reduce the number of features
C based on a percentage of Sz
D a special type of nesting index
Question 8: Which of the following statements about volume parameters are true?
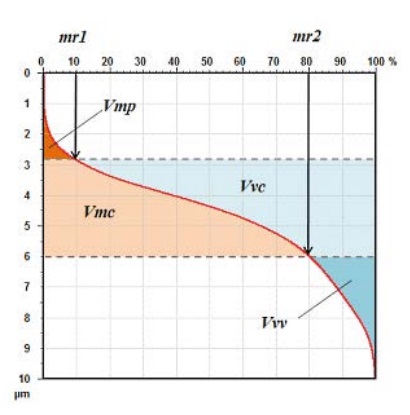
A Vmp could be used in replacement of Spk
B Volume parameters contain material and void volume
C The value of Vmc is always greater than the value of Vmp
D Volume parameters are calculated from the Abbott curve
Question 9: Which surface characteristics are assessed with Str?
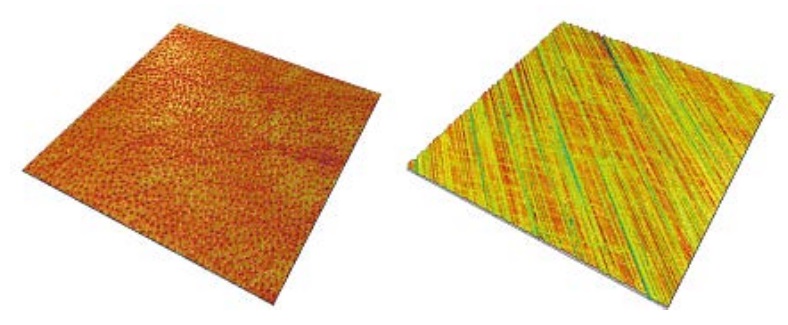
A Surface complexity
B Surface isotropy
C Surface flatness
D Surface smoothness
Question 10: Which of the following statements about saddle points are true?
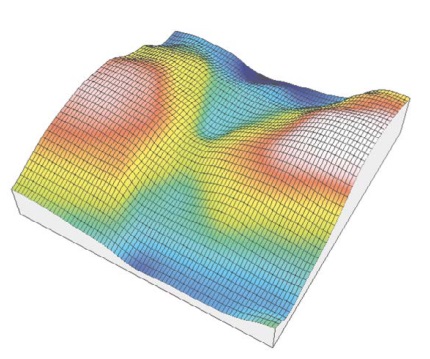
A They are located at the intersection of a course line and a ridge line
B They are points where all downward paths converge
C They are points used in the pruning process
D They are points located exactly between a peak and a pit
Resources & answers
You will find help on the questions in this quiz, as well as a wealth of other information on surface metrology, within the pages of the Digital Surf Surface Metrology Guide
See the answers on Solutions of the Surface Metrology Quiz
Do you want more? Go test the Metrology Quiz #2