Solutions of the Surface Metrology Quiz #2
Find here the solutions of the Surface Metrology Quiz with explanations and justifications. Do not read this page if you did not do the quiz. Try it on Surface Metrology Quiz #2
Question 1: Which parameter is best suited for controlling the sealing efficiency of a gasket?
Correct answer: C
From the four proposed parameters, the most efficient for sealing applications is Wt, calculated on the waviness profile. Using a waviness parameter has the advantage of removing local roughness, scratches and focusing on form deviation and long wavelengths that may affect contact.
Rq is a roughness parameter averaging height differences from the waviness reference profile. It does not take into account variations of form and cannot be used in sealing applications.
Pz is calculated on the primary profile which contains the waviness profile. However, it may be affected by local scratches and peaks that would mask potential form deviations.
RSm is a spacing parameter measuring the mean width of profile elements on the roughness profile along the X axis. It does not tell anything about the Z axis.
Question 2: Which parameter is the most sensitive to outliers?
Correct answer: C
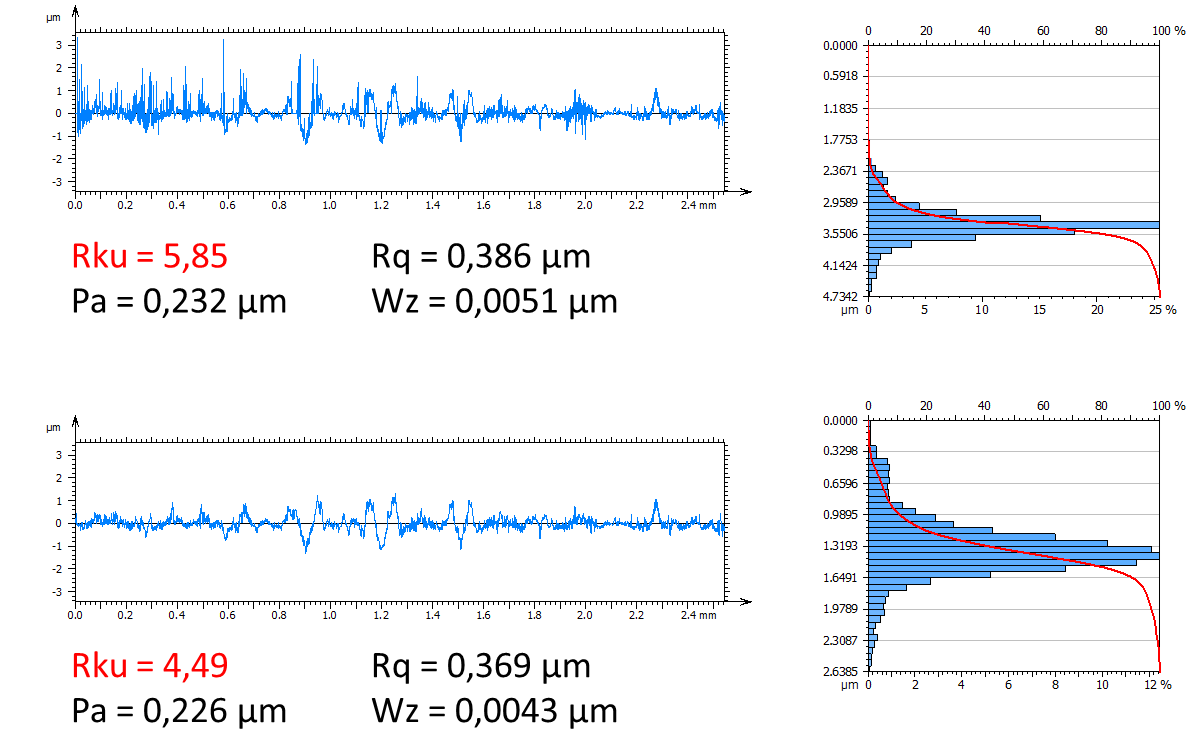
Rku is the fourth statistical moment, which means that its equation includes a power of four on the height deviations. The higher the power, the more sensitive to outliers. The illustration below shows a noisy profile with numerous outliers and its cleaned version with outliers removed. We see that the other parameters are only slightly changed but Rku is dramatically different. The variation on Wz is also quite high but it is because the waviness profile is almost flat in this example.
Question 3: Which of the following parameters can be used to control lubrication efficiency?
Correct answers: B, C
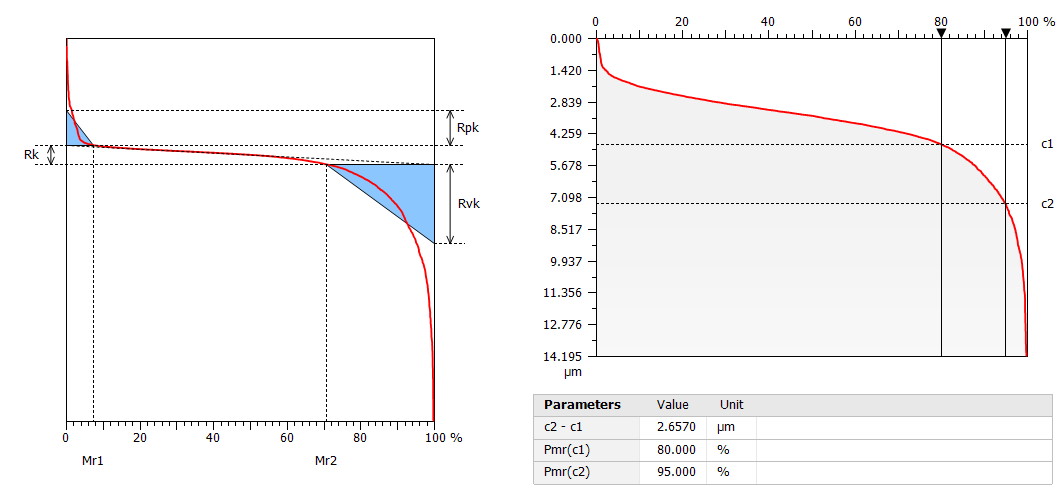
Rvk is typically the recommended parameter for studying lubrication. It can be seen as an oil retention volume parameter, although is does not calculate a volume.
Rdc can also be used for lubrication if its attributes are configured correctly, for example with Rdc(80%, 95%) so it focuses on the bottom part of the profile.
Rv measures the height of valleys but takes into account only one point per sampling length, which may be a scratch. So it is not suitable for lubrication.
Rpk focuses on peaks, not valleys, so it is meaningless for lubrication.
Question 4: Which of the following filtration conditions are best suited for the calibration of the horizontal amplification coefficient on a profilometer?
Correct answers: A, C
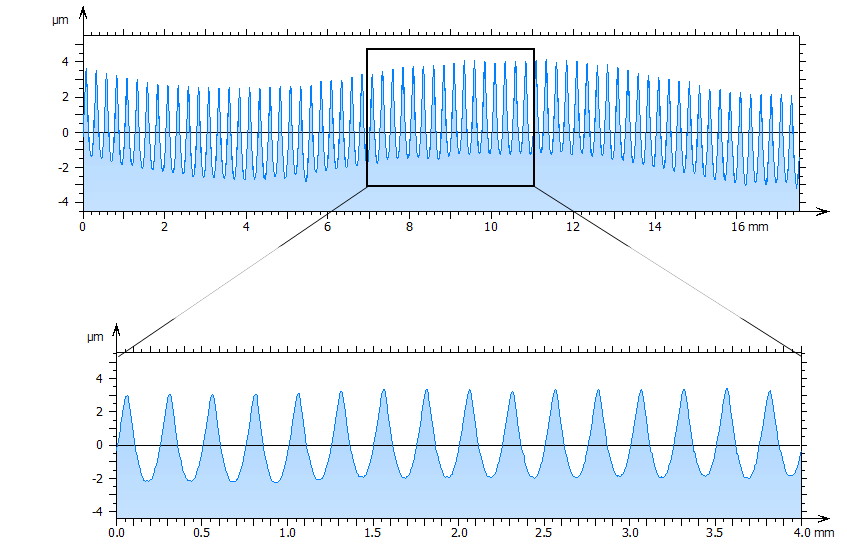
Using a periodic calibration specimen with a known period makes it possible to calibrate the X-axis of a profilometer using a spacing parameter such as RSm.
A roughness filter with a cut-off equal or larger to 0.8 mm will ensure that the waviness is removed and the periodical pattern not affected by the filter. Therefore all periods will be correctly aligned and a spacing parameter will provide an accurate value. With a shorter cut-off, the periods will start to be affected by the filter and the period may be altered.
A waviness filter will only retain the large modulation with a period of around 10 mm and will remove almost totally the periodical pattern of interest, so the calibration cannot be done.
Question 5: Which of the following statements are true?
Correct answers: B, C, D
The λs filter is not mandatory but is defined by default, i.e. if no other indication is given.
According to VDA2006, a German standard for the automotive industry, the λs filter is prohibited on profile parameters, because it removes high-frequency information that may be of interest. However, by default and according to ISO, the λs filter is usually applied.
On a waviness profile, the filter will keep wavelengths longer than the cut-off value, so there is no obligation to apply the λs filter as it is much smaller and the λc filter will anyway remove the wavelengths that are normally removed by the λs filter.
A filter always removes information, and sometimes it is useful information. A S Filter on a surface may alter the information content much more dramatically than a λs filter on a profile (which usually has a smaller spacing).
See the page Filtration techniques for Surface Texture
Question 6: Which of the following parameters are calculated from an autocorrelation function?
Correct answers: B, C
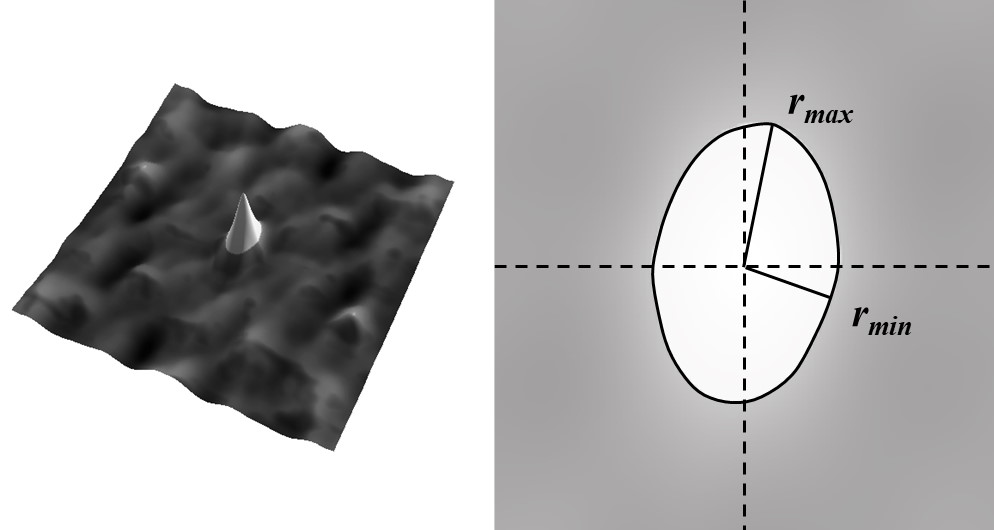
Sal and Str are both calculated from an autocorrelation function. Sal is the smallest radius (r
Std is the texture direction, calculated from the Fourier spectrum. Sfd is the fractal dimension and has nothing to do with autocorrelation.
Question 7: Which of the following methods are related to fractal analysis?
Correct answers: A, B, C, D
Morphological envelopes are calculated from closing and opening morphological filters with a structuring element. This method can be used in fractal analyses, by iterating the size of the structuring element and calculate the volume enclosed between the envelopes. A log-log graph can be built of the volume in function of scale (size of structuring element)
Length-scale and Area-scale are two methods of the Scale-Sensitive Fractal Analysis (SSFA) used to establish functional correlations on profiles and surfaces.
The box method is one of the first fractal analysis that was invented but it is not so much popular nowadays.
See the page Scale-Sensitive Fractal Analysis
Question 8: Which of the following parameters are not defined in ISO 25178?
Correct answers: A, C
The correct answers are the parameters that are not defined in ISO 25178. Sbi was part of the European Report EUR 15178N that was in use before the ISO standard was developed. The three indices Sbi, Sci and Svi are now replaced by Volume parameters. S3z does not exist but R3z was a parameter defined by Daimler in a attempt to have a more robust Rz.
Sdv is a Feature parameter used to calculate the volume of significant dales. S5v is the mean depth of the 5 most significant pits (valleys).
See the page Introduction to Surface Texture and the page Areal Feature parameters
Question 9: Which of the following parameters are Feature parameters?
Correct answers: A, B, D
Spc is the mean curvature of the significant peaks. Sda is the mean area of the significant dales. Spd is the density of significant peaks. All these three parameters are Feature parameters defined in ISO 25178-2.
Std is the texture direction and is a field parameter.
See the page Areal Feature parameters
Question 10: Which famous metrologist once spoke about "parameter rash"?
Correct answer: B
The well-known Professor David Whitehouse wrote a famous article in 1982, The parameter rash - is there a cure? where he condemned the increasing number of profile parameters. The idea behind was that the more parameters we defined, the more difficult for users to learn how to use them. However, parameters are defined for a wide variety of applications but you usually need only 2 to 5 parameters for a given application, and most of the time you retain the most suitable in specifications.
See the paper The parameter rash - Is there a cure?